Micropipettes
Micropipettes are precision instruments used to measure and transfer small volumes of liquid, typically in the microliter range, essential for accurate and reproducible laboratory experiments.
UW-Stout's Biotechnology Lab is an advanced lab space dedicated to advancing the understanding and application of biotechnological processes. This lab serves as both an academic space and a center for research, where students from diverse fields get hands-on in real-world research and applications. Projects range from cloning zebrafish genes to creating transgenic models for studying human diseases, the lab supports both educational and research missions. It is integral to UW-Stout’s commitment to applied learning and research, providing the necessary tools for students and faculty to push the boundaries of biotechnology while performing industry-focused scientific research.
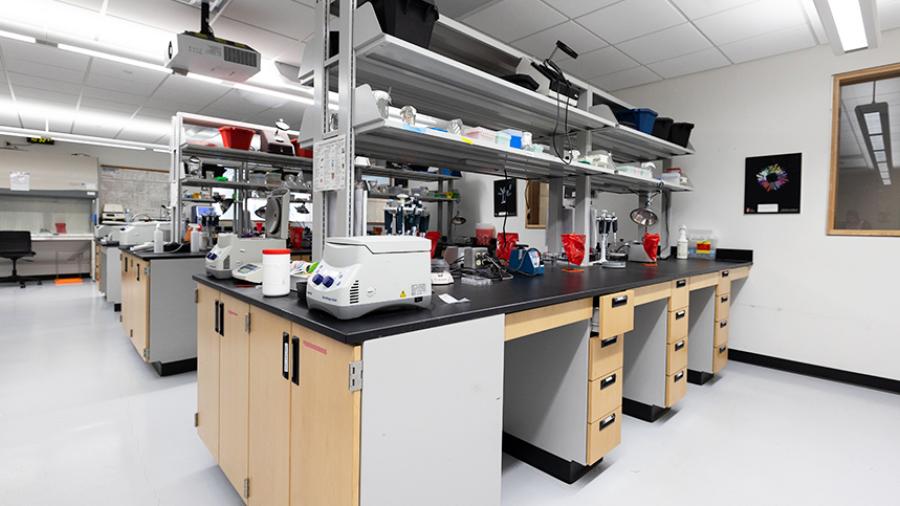

At UW-Stout's Biotechnology Lab, students have access to interdisciplinary research opportunities, from genetic engineering to environmental biotechnology, equipping them for diverse career paths. The lab features industry-standard equipment, including PCR machines, gel electrophoresis systems, and CO2-controlled tissue culture incubators, enabling sophisticated scientific experiments. Additionally, the lab promotes professional development through industry-sponsored projects and exposure to real-world challenges, while also fostering community engagement through outreach programs that offer hands-on learning experiences for high school students and other visitors.
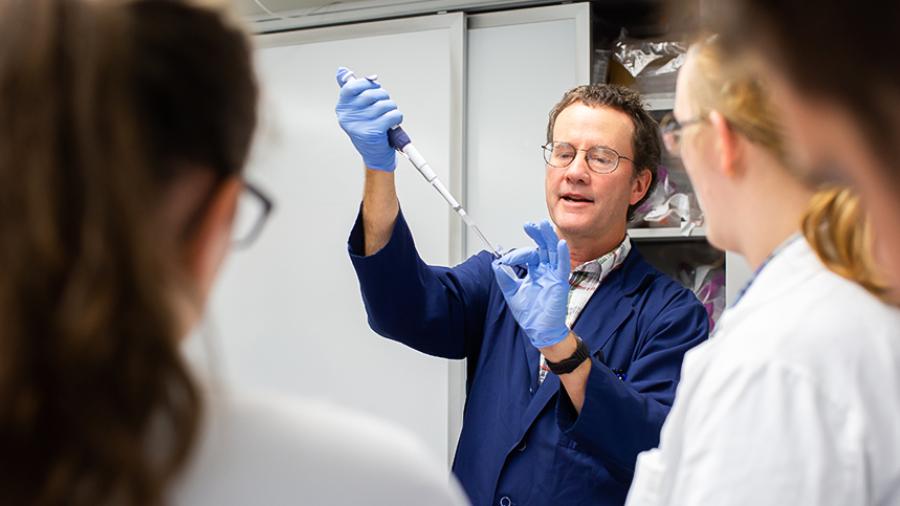


Micropipettes are precision instruments used to measure and transfer small volumes of liquid, typically in the microliter range, essential for accurate and reproducible laboratory experiments.
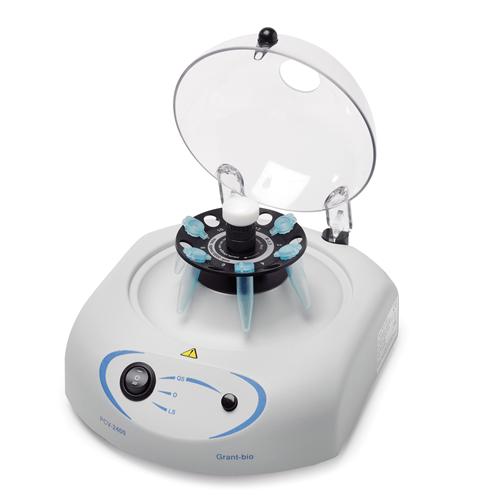
Vortexers are devices used to mix small vials of liquid quickly and thoroughly by creating a vortex motion. They are commonly used to ensure homogeneity in samples before analysis.

Centrifuges are machines that spin samples at high speeds to separate components based on density. They are used for tasks like pelleting cells, clarifying solutions, and separating blood components.
A compact microcentrifuge ideal for quick and efficient separation of small sample volumes, widely used in molecular biology.

A water bath is laboratory equipment that maintains a constant temperature by heating water. It is used to incubate samples at specific temperatures for extended periods, such as in enzyme reactions and bacterial culture growth.

PCR machines, or thermal cyclers, are used to amplify DNA sequences through the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process, cycling through specific temperature changes for denaturation, annealing, and extension.
A high-performance thermal cycler known for its precise temperature control and fast cycling times, ideal for efficient DNA amplification.

NanoDrop spectrophotometers measure the concentration and purity of nucleic acids and proteins using very small sample volumes. They are crucial for assessing sample quality before further molecular biology procedures.
Gel electrophoresis equipment is used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge by applying an electric field to a gel matrix. This method allows for the analysis and purification of specific nucleic acid fragments or proteins.
A Gel Doc system is an imaging device used to visualize and document the results of gel electrophoresis. It captures images of stained gels, allowing for the analysis and quantification of separated DNA, RNA, or protein bands.

Western blot imaging systems detect and visualize proteins transferred to a membrane after electrophoresis. These systems often use chemiluminescence, fluorescence, or colorimetric detection methods.
A specialized imaging system for detecting proteins on western blots using chemiluminescence, providing high sensitivity and accurate quantification of protein bands.
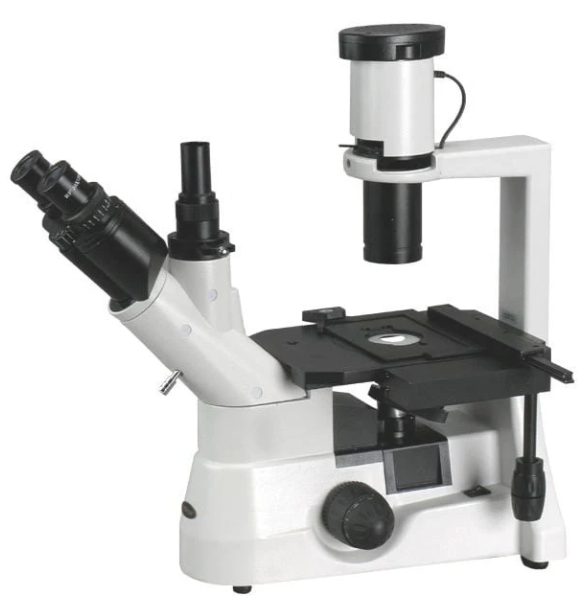
An inverted microscope is designed with the light source and condenser above the specimen and the objectives below. This configuration allows for the observation of living cells or organisms in a culture dish, making it ideal for cell culture and tissue studies.

A biological safety cabinet (BSC) is a ventilated enclosure designed to protect laboratory personnel, the environment, and samples from exposure to infectious or hazardous aerosols and splashes. BSCs provide a sterile workspace for safely handling pathogens and other biohazardous materials.

CO2-controlled tissue culture incubators maintain optimal conditions for the growth of cell cultures by regulating temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels. These incubators are essential for culturing mammalian cells and other organisms that require precise environmental control.